How to Integrate AI Tools for Code Reviews on GitHub
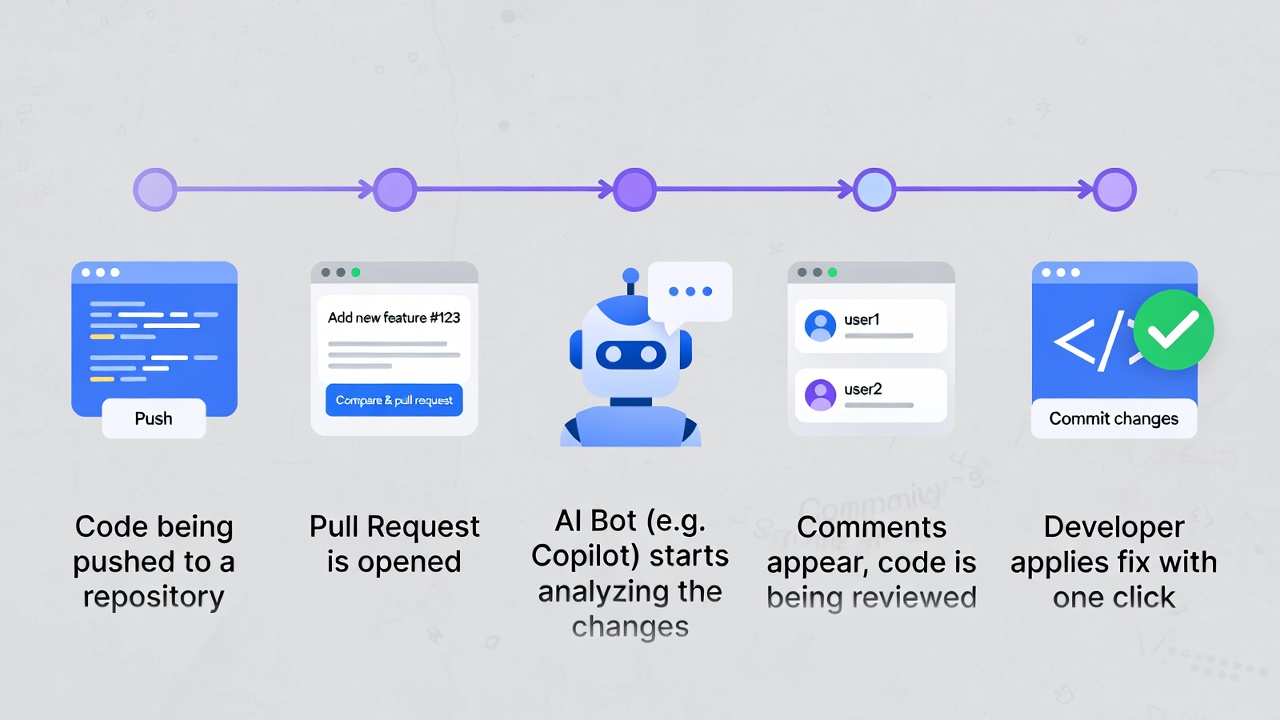
Code reviews are a key part of building good software. When you or your team push changes to a shared project on GitHub, someone looks over the code in a pull request (PR) to spot mistakes, suggest better ways to write it, check for security problems, and make sure it fits the project's style. It's like having a second pair of eyes proofread your work before it goes live.
But doing reviews by hand takes time. Busy teams often skip deep checks, miss bugs, or argue over small things. That's where AI tools come in. These smart helpers scan your code automatically when you open a PR. They point out issues fast, suggest fixes, and even explain why something might be better another way. Many connect right into GitHub so you see their notes as comments on the PR page.This guide walks you through everything from scratch. In many teams, these automated reviews are part of a larger CI/CD pipeline that runs tests, checks, and security scans before code is merged.
We'll cover why AI helps, pick the best tools for most people, show exact setup steps for the top ones (GitHub Copilot, CodeRabbit, and a couple more), share tips to use them well, and talk about common problems and fixes. By the end, you'll know how to add AI reviews to your GitHub workflow and save hours each week. No coding experience with AI needed, we'll keep it simple with clear steps and examples.
Why Code Reviews Matter and How AI Makes Them Easier
Think of a GitHub repository as a shared notebook where your team writes code together. A pull request is when one person says, "Hey, I added this new feature, check it before we add it to the main notebook." Reviewers read the changes (called diffs), test mentally or locally, and leave comments like "This loop could be faster" or "Add a check for empty input here."Without reviews, bugs slip in. Small teams might review everything, but as projects grow, PRs pile up. People get tired, miss edge cases, or overlook style rules.AI changes that. These tools use large language models (the tech behind ChatGPT-like systems) trained on tons of code. They understand context across files, spot patterns that lead to bugs, suggest cleaner code, check for security holes like SQL injection or leaked keys, and even enforce your team's coding standards.
Real benefits include:
- Speed: A review that takes a human 30 minutes might come back in seconds.
- Consistency: AI doesn't forget rules or have bad days. It applies the same checks every time.
- Learning: New developers get instant feedback and explanations, like having a patient mentor.
- Scalability: Big teams with hundreds of PRs per day can still review thoroughly.
- Security boost: Many tools scan for vulnerabilities automatically, catching things humans might overlook.
- Less burnout: Humans focus on big-picture logic and architecture instead of spotting typos or style issues.
Of course, AI isn't perfect—it can miss context unique to your project or suggest something that works but isn't the best fit. That's why you always combine it with human oversight. 1
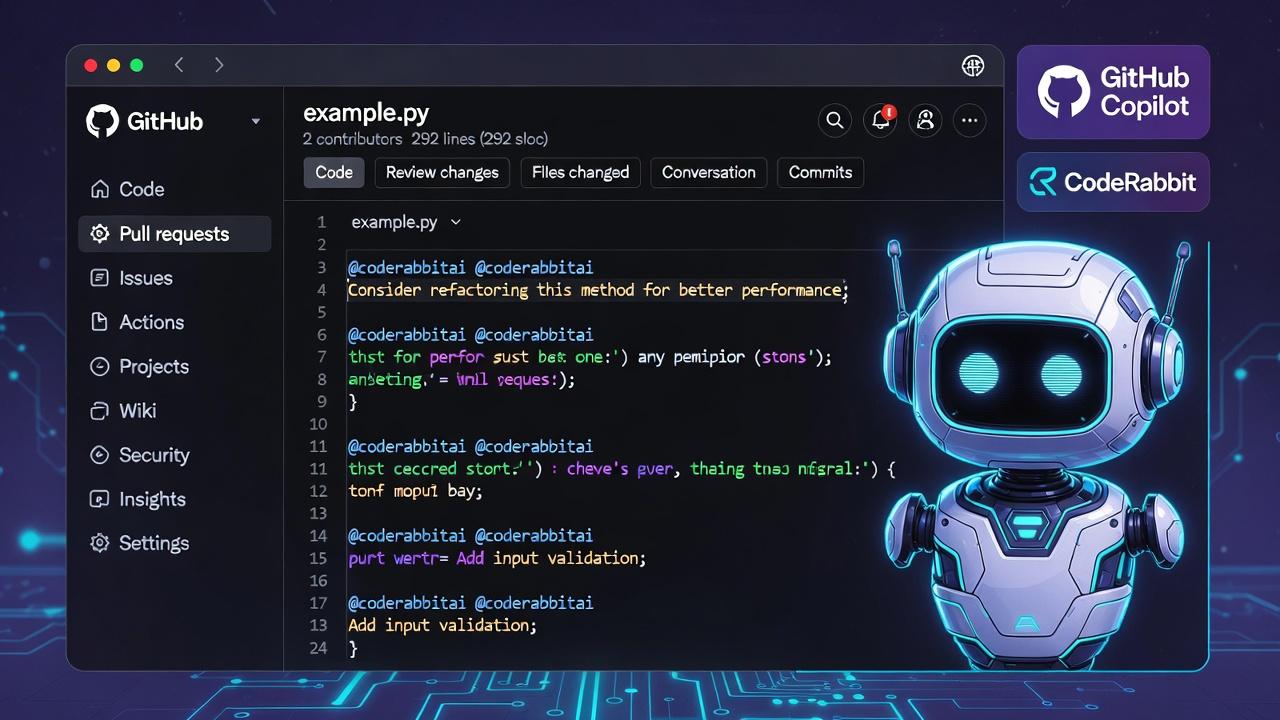
In GitHub specifically, AI tools show up as comments from a bot account (like @github -copilot or @coderabbitai) right in the PR. You can reply to them, apply suggested changes with one click, or ask for more details.
Key Benefits of AI-Assisted Code Reviews on GitHub
Beyond speed, here's why teams adopt these tools:
- Catch issues early: AI scans the whole PR context, including related files, not just the changed lines.
- Improve code quality: Suggestions for refactoring, better variable names, or performance tweaks help over time.
- Security and compliance: Tools flag secrets, outdated libraries, or policy violations.
- Team knowledge sharing: Explanations in comments teach best practices without meetings.
- Cost savings: Fewer bugs in production mean less firefighting and happier users.
- Accessibility: Junior devs or solo developers get pro-level reviews without a senior always available.
Studies and developer surveys (from sources like GitHub's own reports and tool comparisons) show teams using AI reviews merge PRs faster with higher quality. One common stat: review time drops 50% or more while bug detection rises.2
But remember, AI complements humans, it doesn't replace the final "Approve" button.
Popular AI Code Review Tools for GitHub in 2026
Many options exist. Here are standout ones that integrate well, based on features, ease of setup, and developer feedback. We'll focus on those with strong GitHub support.
1. GitHub Copilot Code Review (Native to GitHub, premium)
-
Built-in feature from GitHub. Reviews PRs, gives feedback, and suggests code changes you can apply directly.
-
Great for: Teams already using Copilot for coding assistance. Supports many languages.
-
Pricing: Part of Copilot Pro, Business, or Enterprise plans (per-user monthly fee). Some organization setups allow use without individual licenses but with quotas.3
2. CodeRabbit
-
Dedicated AI bot that posts detailed PR summaries, walkthroughs, and line-by-line suggestions. You can chat with it via comments.
-
Great for: Fast feedback and iterative improvements (it can even generate fix branches).
-
Free tier available; paid for advanced features like more checks or priority support.4
3.Sourcery
-
Focuses on Python (strong) and other languages. Provides instant PR reviews with refactoring suggestions.
-
Great for: Python-heavy projects wanting quick, actionable improvements.
-
Integrates via GitHub app; free for open source, paid plans for private repos.5 !
4. Qodo (formerly CodiumAI)
-
PR-AgentOpen-source friendly agent. Run commands like /review or /improve on PRs for analysis, tests, and more.
-
Great for: Customizable, self-hosted, or budget-conscious teams. Works in GitHub, IDEs.
-
Free core (open-source), enterprise options.6
5. Snyk Code
-
Security-first with AI-powered deep code scanning. Shows vulnerabilities in PRs with fix suggestions.
-
Great for: Apps handling sensitive data or needing compliance (GDPR, etc.).
-
Free for open source; paid for teams. Integrates via GitHub Marketplace or Actions.7
- Others worth noting: CodeAnt AI (full health checks), Codacy/SonarQube (static analysis + AI), Graphite Agent (platform-level automation).89
Start with GitHub Copilot or CodeRabbit if you're new, they're straightforward.
Step-by-Step: Set Up GitHub Copilot Code Review
Prerequisites:
- A GitHub account (personal, org, or enterprise).
- Copilot enabled on your plan (Pro+ recommended for full features).
- For orgs: Admin must turn on relevant policies.
Manual Review (Quickest Start):
- Go to your repository on GitHub.com.
- Open or create a pull request.
- In the right sidebar, under Reviewers, click the people icon or "Add reviewers".
- Select Copilot (it appears if enabled).
- Wait ~30 seconds—Copilot analyzes changes, dependencies, and context.
- Scroll to its comment section. Read feedback, thumbs up/down to train it, or apply suggested code diffs (green "Apply" buttons).
- To re-review after edits: Go back to Reviewers menu and request Copilot again. 10
Copilot leaves a "Comment" review (not blocking approval). It may integrate static tools like CodeQL (security) or ESLint (linting) for better accuracy. Excludes big files like package-lock.json.
Automatic Reviews:
- Personal: Profile > Copilot settings > Enable "Automatic Copilot code review".
- Repository: Repo Settings > Rules > Rulesets > New branch ruleset > Target branches (e.g., main) > Enable "Automatically request Copilot code review". Choose to review new pushes or drafts.
- Organization: Org settings > Repository rulesets > Similar setup with patterns for repos/branches.
Customize with a .github/copilot-instructions.md file in your repo root. Add natural language rules like "Prefer functional programming in JS" or "Always validate inputs." Path-specific files in .github/instructions/ for folders.11
Using Suggestions: Click "Implement suggestion" (public preview feature) to let Copilot agent create a new PR with fixes. Great for quick wins.
Limitations: Quota-based (premium requests); doesn't auto-approve; may repeat comments on re-review; humans must validate.12
This native option feels seamless, no extra accounts.
Step-by-Step: Integrate CodeRabbit with GitHub
CodeRabbit shines for conversational reviews.
-
Go to CodeRabbit website and sign up (GitHub login easy).
-
In dashboard, click "Add Repositories".
-
Choose "Only select repositories" > Pick your repo (install the GitHub app if prompted, grant read/write for reviews and optional PR creation).
-
Authorize. CodeRabbit won't store your code long-term.
Test It:
- In your repo, create a branch (e.g., feature/new-util).
- Add a sample file with intentional issues, like a Python function missing returns or docstrings.
- Commit and open a PR to main.
- Wait moments: @coderabbitai
- posts:PR summary (if none provided).
- "Walkthrough" comment analyzing changes.
- Detailed review comments on lines/files with suggestions.
Interact:
- Reply on PR: @coderabbitai explain this suggestion or @coderabbitai generate docstrings.
- It can create a new branch/PR with fixes.
- For config: Add .coderabbit.yaml for rules, ignore paths, or custom prompts.
Cleanup: Delete test repo or remove app access. Works on private/public repos. Free tier suffices for basics; upgrade for heavier use or more languages.13
Quick Setups for Sourcery and Qodo PR-Agent
Sourcery:
- Sign up at sourcery website
- Install GitHub app or connect repos.
- It auto-reviews every PR with suggestions (refactors, Python-focused).
- Apply changes via GitHub interface or CLI.
- Customize via config file for your style.14
Qodo PR-Agent (Open-Source Option):
-
Install via GitHub Marketplace or self-host (uses your API keys for models like OpenAI/Claude).
-
Add to repo as GitHub App.
-
On PR, comment
/reviewfor full analysis,/improvefor suggestions,/askfor questions. -
Configurable via YAML for focus areas (tests, security).
-
Free to run; great for control and no vendor lock-in.15
Security-Focused: Snyk Code Integration
For vulnerability reviews:
-
Sign up at snyk website, connect GitHub (install app for repo access).
-
Import repos or use GitHub Actions workflow to scan on PR open/push.
-
Snyk posts security findings as PR checks/comments with severity and fix PRs.
-
Enable Snyk Code for AI-deep static analysis.
-
Use in CI/CD to block merges on high-severity issues.16
Build Your Own with GitHub Actions + AI APIs
Want full control or specific prompts? Use GitHub Actions. GitHub Actions is one of the most popular CI/CD tools today, but it’s not the only option. Many teams still compare it with Jenkins when deciding how to automate reviews and deployments.
Example workflow (.github/workflows/ai-review.yml):
name: AI Code Reviewon:pull_request:types: [opened, synchronize]
jobs:review:runs-on: ubuntu-lateststeps: - uses: actions/checkout@v4with:fetch-depth: 0 # Full history for context
- name: Get PR diff id: diff run: | git fetch origin ${{ github.event.pull_request.base.ref }} echo "diff<<EOF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT git diff origin/${{ github.event.pull_request.base.ref }}...HEAD >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT echo "EOF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: AI Review with OpenAI uses: actions/github-script@v7 with: github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} script: | const diff = ${{ steps.diff.outputs.diff }}; // Call OpenAI API (use secret key) or Grok/xAI API // Prompt: "Review this diff for bugs, style, security. Suggest fixes. Be concise." // Post as PR comment using GitHub APIStore API keys in repo secrets. Use libraries like openai Python package in a step. Customize prompt for your stack (e.g., "Focus on TypeScript React best practices"). Test locally first. This way, you pick the model (GPT, Claude, local LLMs) and add rules. Costs depend on API usage but flexible.17
Best Practices to Get the Most from AI Reviews
-
Always human-review: Treat AI comments as starting points. Verify suggestions, test them, and understand why.
-
Provide context: Use custom instructions or PR descriptions. Good titles/descriptions help AI.
-
Iterate: Reply to bots, give feedback (thumbs, comments) so they improve.
-
Combine tools: Copilot for general + Snyk for security.
-
Privacy first: Check what data tools access/store. Most don't keep your code after review.
-
Start small: Test on one repo or low-stakes PRs.
-
Measure: Track review time, bug rates before/after.
-
Team buy-in: Train everyone; set guidelines like "AI must be reviewed before merge."
-
Handle false positives: Tune configs to reduce noise.
Use AI for routine checks so humans focus on design, architecture, and business logic.18

Common Challenges and Solutions
-
Hallucinations/wrong suggestions: Solution: Cross-check, use deterministic tools alongside (linting, tests).
-
Cost/Quotas: Monitor usage; start with free tiers; self-host open-source.
-
Context limits: Break big PRs; provide more repo context via instructions.
-
Setup hurdles: Follow official docs; use test repos.
-
Over-reliance: Mandate human approval; review AI suggestions as part of onboarding.
-
Language support: Most cover popular ones (JS, Python, Java, etc.); check for yours.
Data security: Reputable tools (GitHub, CodeRabbit) are SOC 2 compliant and delete data post-review.
Comparison of Top Tools
| Tool | GitHub Integration | Key Strengths | Pricing | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GitHub Copilot | Native PR menu/auto rulesets | Suggestions apply easily, static tool blend | Subscription(Pro+) | Github-native teams |
| CodeRabbit | App bot + @mentions | Conversational, generates fix PRs | Free tier + paid | Interactive feedback |
| Sourcery | App for PRs | Refactoring focus (esp. Python) | Free OSS, paid private | Refactoring-heavy codebases |
| Qodo PR-Agent | Commands or app | Open-source, customizable | Free/self-host | Control & budget |
| Snyk Code | Actions/checks | Security/vuln deep scan | Free OSS, team plans | Secure apps |
Real-World Example
Suppose you add a login function. AI might flag: "Missing rate limiting, vulnerable to brute force. Consider adding Redis lock." Human reviewer confirms and adds it. Or suggests "Use async/await for cleaner code." You apply, test, and merge faster.Teams report 2-3x faster reviews and fewer post-merge bugs.
Conclusion
Integrating AI tools into GitHub code reviews turns a time-consuming chore into a quick, smart process. Start with GitHub Copilot for simplicity or CodeRabbit for chat-like help. Set it up today on a test repo, experiment, and scale to your workflow. You'll write better code, learn faster, and free up time for creative work.
FAQs
-
Do I need to pay for these tools? Many have free tiers or open-source options. Copilot requires a subscription; CodeRabbit starts free.
-
Will AI replace human reviewers? No. It handles grunt work; humans handle nuance, intent, and final decisions.
-
Is my code private? Top tools process temporarily and delete data. Check each provider's policy.
-
What if the suggestion is wrong? Test it, reject, and provide feedback to improve the model.
-
Can AI review my whole codebase? Some tools offer repo-wide scans; use for onboarding new code.
-
How do I handle large PRs? Split them or use tools that support context well.
-
Supports my language? Most handle 10-20+ popular languages; verify specifics.
-
Can I customize? Yes, config files,
instructions.md, or prompts in custom Actions. -
Integration with IDEs? Many (Copilot, Qodo) work in VS Code/JetBrains too for pre-PR checks.
-
What about GitLab/Bitbucket? Some tools support them; focus here is GitHub.
Windframe is an AI visual editor for rapidly building stunning web UIs & websites
Start building stunning web UIs & websites!