React and Node.js: Mastering Full-Stack Development in 2026

React and Node.js form the backbone of countless modern web applications, powering everything from interactive user interfaces to robust backend services. As JavaScript technologies, they enable developers to create efficient, scalable apps using a single language across the stack. With updates in late 2025 and early 2026 enhancing their capabilities, like React's improved server components and Node's security-focused v24 LTS, they're more relevant than ever for building AI-integrated, real-time experiences.
In this post, we'll cover the basics of each, highlight their key differences, and walk through building a practical app. We'll include real-world examples, tips to avoid common mistakes, and even touch on future directions based on 2026 trends. By the end, you'll have the tools to start experimenting on your own. Let's get started!
The Rise of React and Node.js: A Quick Overview
Before diving deep, let's understand why these two are so popular. React, developed by Facebook (now Meta), launched in 2013 and has since become the go-to for front-end development. As of 2026, over 11 million websites worldwide run on React, powering everything from social media feeds to e-commerce platforms. 1 Meanwhile, Node.js, introduced in 2009, has transformed server-side programming. Today, about 40.8% of developers use Node.js as their runtime environment, making it a staple for backend work. 2
What makes them a perfect match? They both use JavaScript, eliminating the need to switch languages mid-project. This "JavaScript everywhere" approach speeds up development and reduces errors. For instance, companies like Netflix use React for their user interfaces and Node.js for handling massive streaming data loads. In a recent survey, 39.5% of web developers reported using React, often paired with Node.js for full-stack apps. 3
If you're setting up for the first time, grab a free code editor like VS Code from Microsoft's site. You'll also need Node.js installed, it comes with NPM, the package manager we'll use extensively. For a quick install guide, check out the official Node.js documentation.
Demystifying React: Building Interactive Front Ends
React is essentially a JavaScript library for creating user interfaces. Unlike traditional web development, where you might write static HTML pages, React lets you build reusable components that update dynamically. Think of it as assembling a puzzle: Each piece (component) fits together to form the big picture, and if one piece changes, the puzzle adjusts without falling apart.
A Brief History and Evolution
React started as an internal tool at Facebook to handle the complexity of their news feed. It went open-source in 2013, and by 2018, features like Hooks revolutionized how developers manage state and side effects. In 2026, React continues to evolve with improvements in server-side rendering and concurrent mode, making apps faster and more efficient. 4
Core Concepts Explained
At React's heart is the component. A functional component is a simple JavaScript function that returns JSX (a mix of HTML and JS). For example
function Button({ label, onClick }) { return <button onClick={onClick}>{label}</button>;}Here, label and onClick are props, data passed from parent components. State, managed with useState, handles changeable data.
import { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); return ( <div> <p>Count: {count}</p> <Button label="Increment" onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)} /> </div> );}This counter updates in real-time, thanks to React's virtual DOM, which compares changes and updates only what's necessary, far more efficient than reloading the whole page.
Hooks like useEffect run code on mount or updates, perfect for fetching data. Pros of React include its vast ecosystem (think Redux for state management) and community support. Cons? The learning curve for advanced features and potential overkill for simple sites.
Alternatives and When to Choose React
Compared to Vue.js or Angular, React is lighter and more flexible. Vue is great for smaller projects, while Angular offers a full framework with built-in tools. Choose React for SPAs (single-page applications) like dashboards or social apps.
For setup:
Run npx create-react-app my-app.Experiment with a to-do list component to practice.
Common mistake: Forgetting to key list items for efficient rendering.
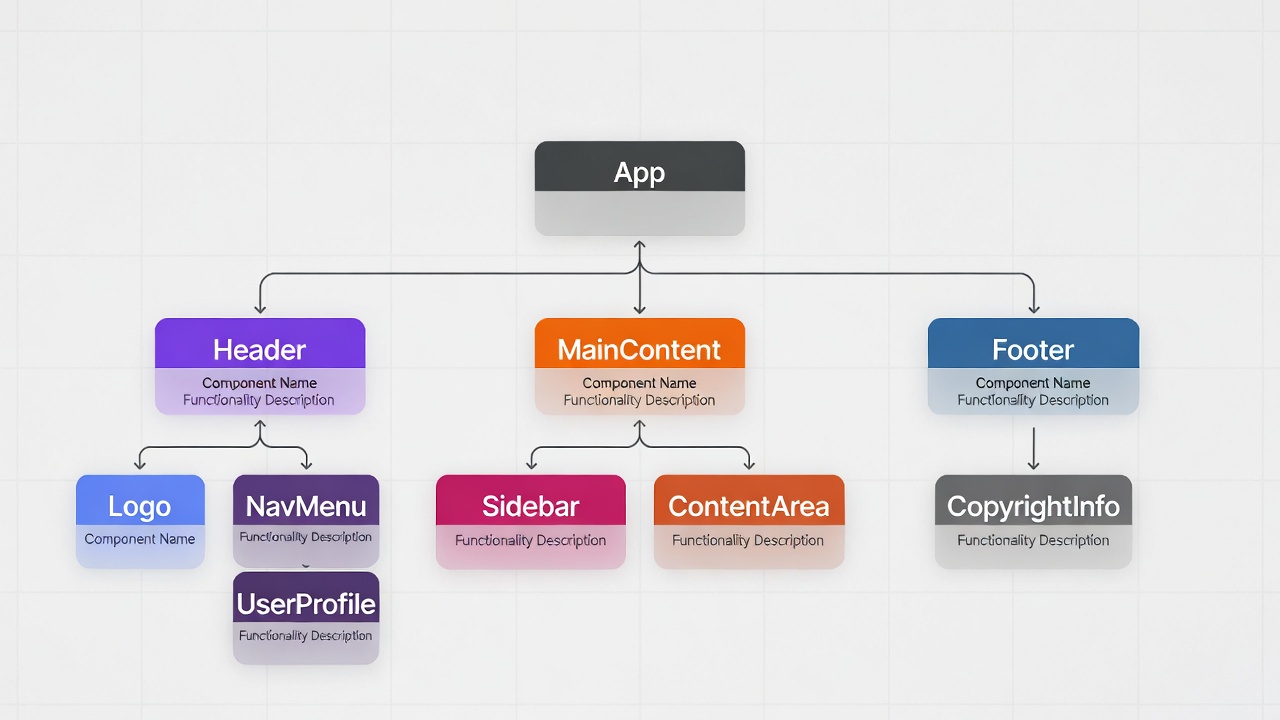
Here's a visual of React's component hierarchy.Dive deeper in the React docs. Or our internal "React Components Mastery" guide.
Exploring Node.js: Powering the Server Side
Node.js flips the script by running JavaScript on servers. Before Node, JS was browser-bound; now, it's a full backend player. It's built on Chrome's V8 engine, making it speedy for I/O-heavy tasks.
Origins and Growth
Ryan Dahl created Node.js in 2009 to solve inefficiencies in traditional servers. By 2026, it's used by 36.42% of professional developers, thanks to its non-blocking nature. It's ideal for real-time apps like chat systems or IoT.
Fundamental Features
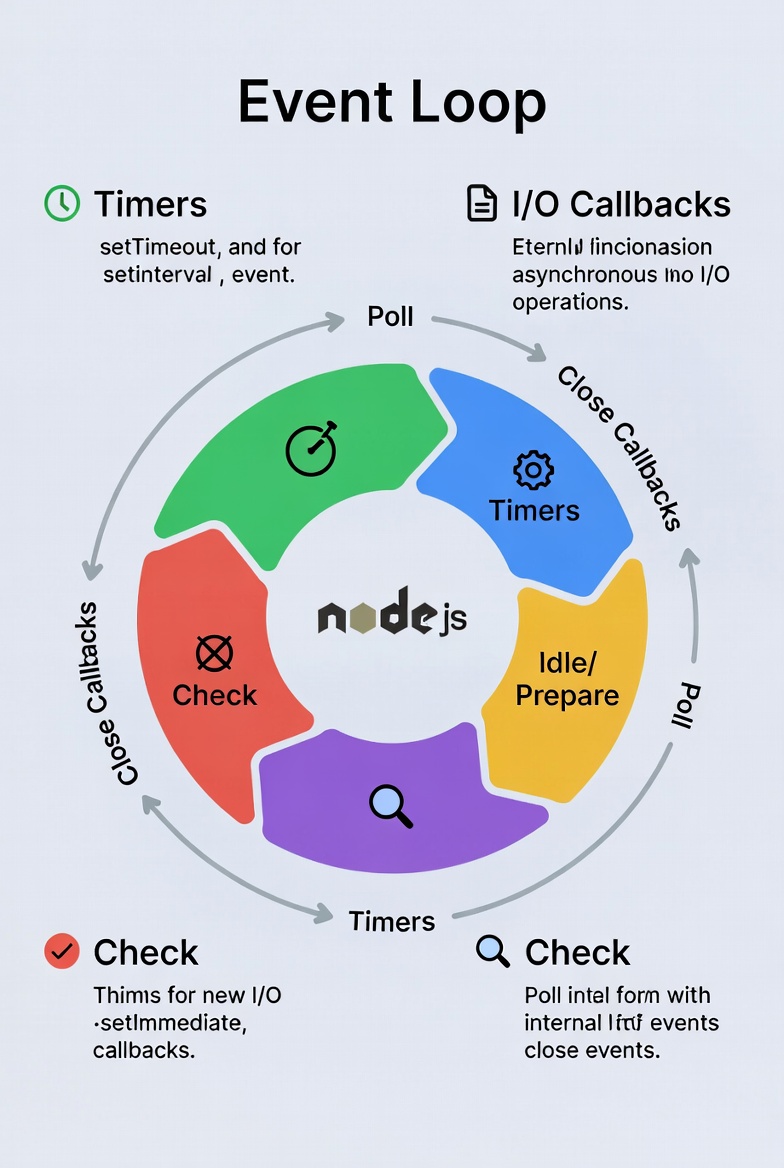
Node's event-driven model means it doesn't wait for tasks, it callbacks when ready. This is like a chef prepping multiple dishes at once. Modules like http create servers easily:
const http = require('http');
http.createServer((req, res) => { res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' }); res.end('Hello from Node!');}).listen(3000);NPM hosts over 2 million packages, from Express for web frameworks to Mongoose for databases.
Pros: Scalability, fast prototyping. Cons: Not ideal for CPU-intensive tasks (use workers for that).
Node vs. Other Backends
Unlike Python's Django or Ruby on Rails, Node is lightweight and async-first. It's great for APIs but might need more setup for structured apps.
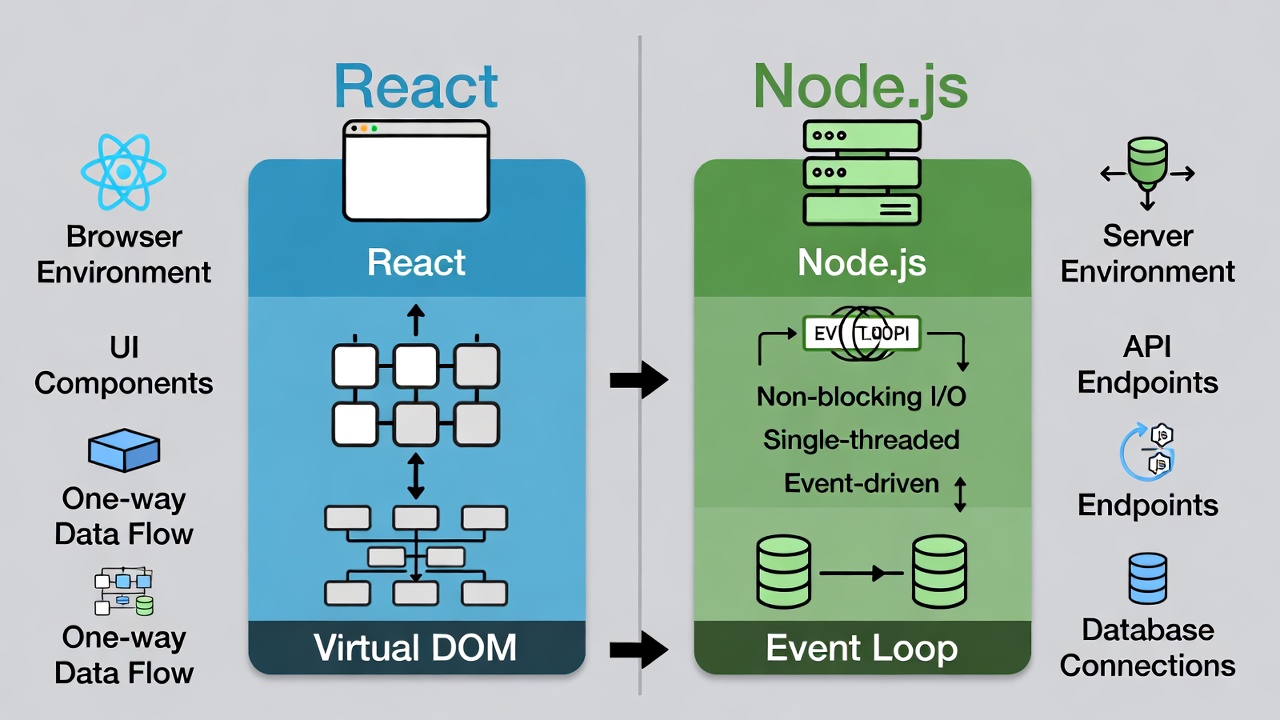
Key Differences Between React and Node.js
While both use JavaScript, React and Node.js serve opposite ends of the stack. Understanding these differences helps you decide when to use each. 6
| Aspect | React.js | Node.js |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Front-end UI library for building interactive interfaces. | Back-end runtime for server-side logic and APIs. |
| Environment | Runs in the browser (client-side), can use server-side rendering. | Runs on servers, handling requests and data. |
| Architecture | Component-based with virtual DOM for efficient updates. | Event-driven, non-blocking I/O for handling concurrency. |
| Use Case | SPAs, mobile apps via React Native, dynamic UIs. | APIs, real-time apps, microservices, database ops. |
| Framework Support | Often with Redux or Context for state. | With Express or Koa for routing |
| Learning Curve | Focuses on UI patterns and state management. | Emphasizes async programming and modules. |
React focuses on "what" the UI looks like, while Node handles "how" the server processes requests. 7 They complement each other in full-stack development, not compete.
Hands-On: Creating a Full-Stack Todo App
Let's combine them in a todo app. This project demonstrates data flow from front to back.
Project Setup
- Create folders: client (React) and server (Node). In client:
npx create-react-app .In server:
npm init -y, npm i express cors mongoose- Connect to MongoDB (install locally or use cloud).
Backend with Node.js
server.js:
const express = require('express');const cors = require('cors');const mongoose = require('mongoose');const app = express();
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/todos', { useNewUrlParser: true });
const TodoSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ text: String, completed: Boolean });const Todo = mongoose.model('Todo', TodoSchema);
app.use(cors());app.use(express.json());
app.get('/todos', async (req, res) => { const todos = await Todo.find(); res.json(todos);});
app.post('/todos', async (req, res) => { const todo = new Todo({ text: req.body.text, completed: false }); await todo.save(); res.json(await Todo.find());});
app.put('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => { await Todo.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, { completed: req.body.completed }); res.json(await Todo.find());});
app.delete('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => { await Todo.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id); res.json(await Todo.find());});
app.listen(5000, () => console.log('Server running on 5000'));This adds CRUD operations.
Frontend with React
In App.js, use Axios for API calls:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';import axios from 'axios';
function App() { const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]); const [newTodo, setNewTodo] = useState('');
useEffect(() => { fetchTodos(); }, []);
const fetchTodos = async () => { const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:5000/todos'); setTodos(res.data); };
const addTodo = async () => { await axios.post('http://localhost:5000/todos', { text: newTodo }); setNewTodo(''); fetchTodos(); };
const toggleComplete = async (id, completed) => { await axios.put(`http://localhost:5000/todos/${id}`, { completed: !completed }); fetchTodos(); };
const deleteTodo = async (id) => { await axios.delete(`http://localhost:5000/todos/${id}`); fetchTodos(); };
return ( <div> <h1>Todo App</h1> <input value={newTodo} onChange={e => setNewTodo(e.target.value)} placeholder="New todo" /> <button onClick={addTodo}>Add</button> <ul> {todos.map(todo => ( <li key={todo._id}> <span style={{ textDecoration: todo.completed ? 'line-through' : 'none' }}>{todo.text}</span> <button onClick={() => toggleComplete(todo._id, todo.completed)}>Toggle</button> <button onClick={() => deleteTodo(todo._id)}>Delete</button> </li> ))} </ul> </div> );}
export default App;Run both node server.js and npm start in client. Add, edit, delete todos, they persist!
For troubleshooting: Check console for CORS errors. Add basic auth later with JWT.
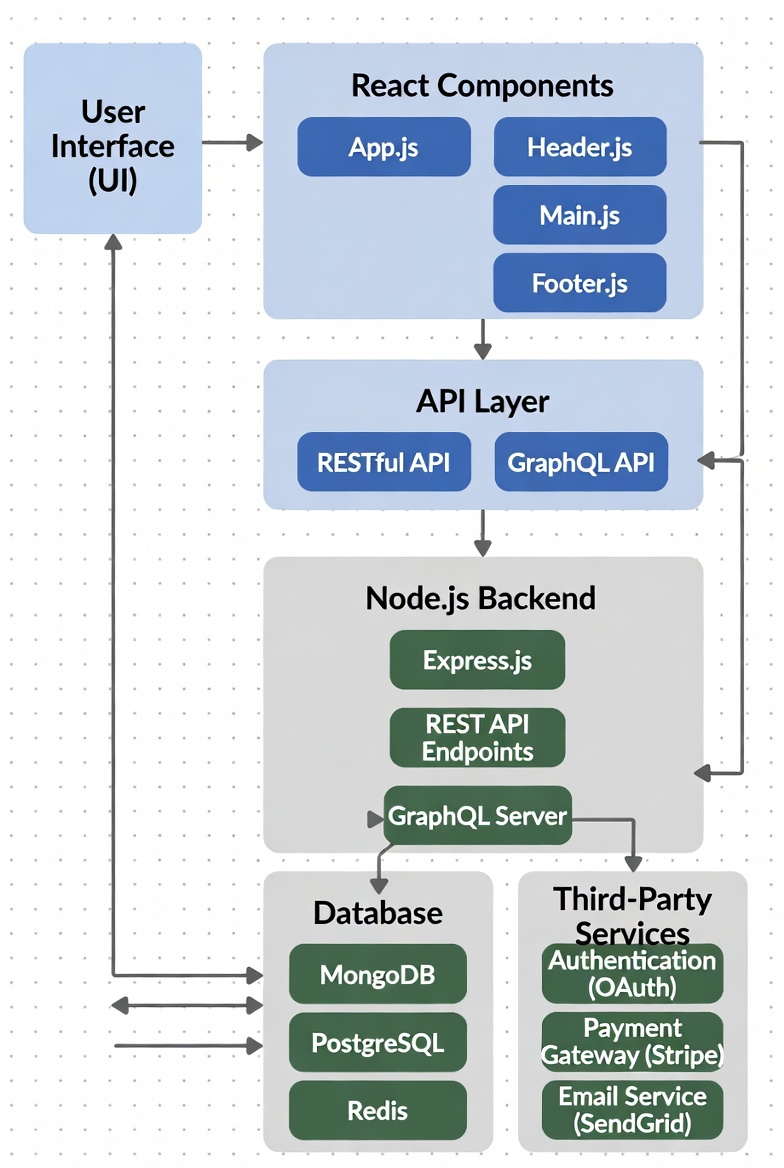
Best Practices, Common Pitfalls, and Performance Tips
To build reliable apps:
- React Best Practices: Keep components pure, use memoization for optimization, handle errors with boundaries.
- Node Best Practices: Use async/await over callbacks, implement logging with Winston, secure with Helmet.
Common pitfalls: In React, infinite loops from useEffect; in Node, unhandled promises causing crashes.
Performance: In React, code-split with lazy; in Node, cluster for multi-core. For scalability, consider Docker for deployment.
Real-World Case Studies and Future Trends
Netflix uses Node for its API layer and React for UI, handling billions of requests. Airbnb leverages React for search interfaces.
In 2026, expect more AI integration in React (e.g., auto-optimizing components) and Node's growth in edge computing. 7
Conclusion
React and Node.js are your gateway to modern web apps, React for engaging UIs, Node for robust backends. In 2026, they're key for AI-enhanced, real-time experiences. Every expert was once a beginner, start small, and practice often.
Windframe is an AI visual editor for rapidly building stunning web UIs & websites
Start building stunning web UIs & websites!